Analog and digital
Analog data :
continuous values
Digital data :
discrete values
Compare :
Information : Analog > Discrete -> Analog have better quality.
Size : Discrete > Analog
Reliably : Discrete > Analog -> Less affected by noise when transmitted.
Analog to Digital
Why?
Because Computers can ONLY work with Digital Data !
How can we do that?
A: Sampling and Quantization.
1. Sampling (取樣) :
第一步,採樣選擇測量連續信號的離散點。
對於" 圖像 ",採樣點在 " 空間 " 上均勻分隔。
對於" 聲音 ",採樣點在 " 時間 " 上均勻分離。
Sampling rate 取樣頻率:一秒鐘有多少個訊號。數值越高,音質越好。
2. Quantization (量化) :
要求每個樣本以固定Bit表示,稱為the bit depth。
Bit depth : 一個訊號用多少個位元記錄。數值越高,音質越好。
Sampling rate :
UnderSampling :
Sampling Rate 跟不上 Signal 的變化
Aliasing (混疊):
兩個不同的正弦波卻有相同的樣本值,導致 discrete signal 不能還原為原本的 signal。
因此有失真的現象。
EX :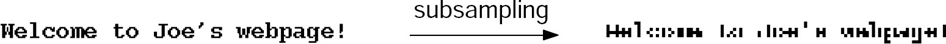
How can we solve this problem ?
A: Nyquist Theorem
★ Nyquist Theorem ★
為了不發生 Aliasing
給定空間或時間的頻率 f
r 為 min sampling rate
r = 2f
Compression :
Compression Rate :
A file that is reduced by compression to " Half " its original size.
rate = 1:2
Types of Compression :
1. Lossless Compression :
先壓縮、再解壓縮,結果還是跟原本資料一模一樣。
Method:
>Run-Length encoding (RLE)
2. Lossy Compression :
先壓縮、再解壓縮,結果跟原本不一樣。
他會減少一些人類無法辨識出來的資訊
Run-Length encoding (RLE) :
方法 :
舉例來說,一組資料串"AAAABBBCCDEEEE",由4個A、3個B、2個C、1個D、4個E組成,經過 RLE
可將資料壓縮為 4A3B2C1D4E
Entropy Encoding
使用較少的 Bits 來對頻繁發生的符號進行編碼,同時對不常出現的符號使用較多 bit
使用 " Shannon’s Equation " 來使我們判斷我們的選擇是不是最好的
S be a string of symbols and p i be the frequency of the ith symbol in the string.
Shannon-Fano Algorithm :
例子 --> 維基百科 : https://goo.gl/gcPPX7
Step 1 : 對於一個給定的符號列表,制定了機率相應的列表或頻率計數,使每個符號的相對發生頻率是已知。
Step 2 : 排序根據頻率的符號列表,最常出現的符號在左邊,最少出現的符號在右邊。
Step 3 : 清單分為兩部分,使左邊部分的總頻率和儘可能接近右邊部分的總頻率和。
Step 4 : 該列表的左半邊分配二進位數字0,右半邊是分配的數字1。這意味著,在第一半符號代都是將所有從0開始,第二半的代碼都從1開始。
Step 5 : 對左、右半部分遞歸應用步驟3和4,細分群體,並添加位的代碼,直到每個符號已成為一個相應的代碼樹的葉。
